Solutions
Horse Construction offers full range of structural strengthening materials with technical supports, documentation supports, products supports, project supports.
The ultimate bearing capacity of concrete beams strengthened with FRP laminate is related to the initial stress level. The ultimate bearing capacity of concrete beams strengthened with FRP laminate is the largest when the initial stress is zero. The loading capacity of beams strengthened with fiber materials is the minimum when loading to 50% without unloading.

1.1 crushing failure of concrete in compression zone
Such destruction includes 2 situations. The first case is that the concrete in the compression area is crushed before the tensile steel reaches its yield. Similar to the over-reinforcement failure of ordinary reinforced concrete beams, this failure is due to the excessive amount of fiber cloth reinforcement and reliable anchorage. This kind of failure steel bar has not yielded, the strength of fiber cloth is far from being fully exerted, and there is hardly any sign of failure when it is destroyed. It has obvious brittleness. The maximum reinforcement of fiber cloth should be strictly controlled in the design to avoid this kind of failure. In the second case, the concrete in the compression zone is crushed after the tensile reinforcement yields, while the fiber cloth has not yet been pulled apart.
1.2 breaking failure of fiber
Under the action of external load, the tensile steel bar yields first, and with the further increase of load, the fiberboard attached to the bottom of the beam is pulled apart, and then the concrete in the compression area is crushed and the beam is completely destroyed. This failure form is called fiber breaking failure. In another case, the tensile steel bar yields first, and then the fiberboard reaches its ultimate tensile strain and breaks, but the concrete in the compression zone is not yet damaged.
1.3 bond failure
Before reaching the normal section bearing capacity, bond failure occurs between the fiber cloth and the adhesive interface. When the failure pattern occurs, there are very few concrete particles on the fiber cloth that is torn off. Adhesive failure is mainly caused by poor performance of glue and poor quality of construction.
1.4 peel failure
Before reaching the normal section bearing capacity, the debonding failure between the concrete and the adhesive interface occurs. The main reason for this failure mode is that the combined action of shear stress and normal stress on the concrete surface causes the generation and expansion of horizontal cracks, leading to the pulling down of concrete, and sometimes even the whole protective layer of concrete beams is pulled down. The peeling failure is mainly due to the fact that the concrete protective layer is too thin or the anchorage measures are not enough. In construction, the thickness of concrete protective layer of steel bar should be guaranteed. In reinforcement design, sufficient anchorage measures should be guaranteed, generally full-length anchorage or additional reliable anchorage measures.

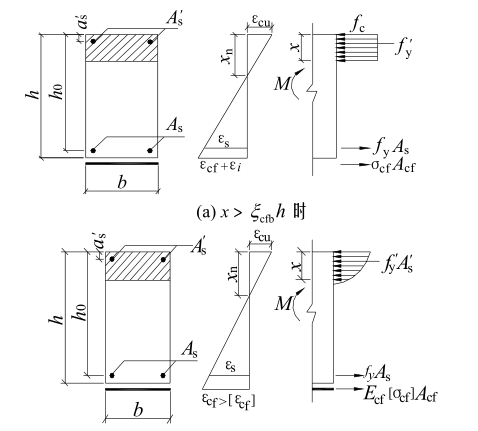
2.Calculation assumption
The experimental study of fiber cloth bending reinforcement shows that the assumption of plane section strain distribution is still used, and the assumption of plane section is also applicable to the incremental distribution of sectional strain in the second stage under secondary loading. The bearing capacity of the reinforced structure is directly related to the stress-strain relationship of the material, the ultimate deformation value of the original structure, and the stress or strain difference between the old and the new parts.
In addition to the basic assumptions in the literature on the calculation of normal section bearing capacity of flexural members, the flexural strengthening with FRP laminate should also meet the following requirements:
(1) When the member reaches the ultimate state of flexural capacity, the tensile strain of the fiber sheet shall be determined on the assumption that the cross-section strain remains flat, but shall not exceed the allowable tensile strain of the fiber sheet.
(2) When considering the influence of secondary force, the plane should be maintained according to the section strain according to the load condition at the time of reinforcement.
The assumption of calculating the initial strain of concrete at the edge of tension zone before consolidation.
(3) the tensile stress of FRP laminate should take the product of elastic modulus and tensile strain of fiber sheet.
(4) There is no bond-peeling failure between fiber sheet and concrete before reaching the ultimate bending capacity.

Conclusion
The ultimate bearing capacity of concrete beams strengthened with FRP laminate is related to the initial stress level. The ultimate bearing capacity of concrete beams strengthened with FRP laminate is the largest when the initial stress is zero. The loading capacity of beams strengthened with fiber materials is the minimum when loading to 50% without unloading. The bearing capacity of CFRP strengthened concrete beams is the highest. The bearing capacity of GFRP strengthened concrete beams is the smallest. The bearing capacity of concrete beams strengthened with hybrid fibers is between two.
You can find anything here you are in need of, have a trust trying on these products, you will find the big difference after that.

High strength, unidirectional carbon fiber wrap pre-saturated to form a carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) wrap used to strengthen structural concrete elements.

High strength carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) strip / laminate / plate for structural strengthening and concrete repair

Prestressed carbon fiber reinforced polymer(CFRP) plate for slab, beam strengthening to increase stiffness, reduce distortion and deflection of members, reduce the cracks, avoid and stop cracking.