Solutions
Horse Construction offers full range of structural strengthening materials with technical supports, documentation supports, products supports, project supports.
bridge reinforcement
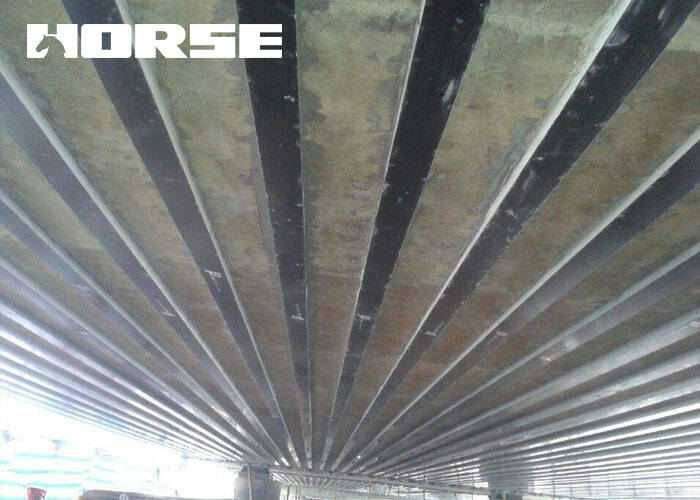

It is the most economical, simplest and most applicable measure to adopt reinforcement methods to improve the bearing capacity, bending resistance, shear resistance and load level of the bridge. Different methods can be adopted according to different bridge status and reinforcement requirements.
1 Technical approaches and design principles of bridge reinforcement
Main technical approach
Bridge reinforcement generally restores or improves the load-bearing capacity of existing bridges through reinforcement of components and improvement of structural performance, so as to extend their service life and meet the requirements of modern transportation.
The main technical ways of its transformation are: strengthening weak components, adding auxiliary components, changing the structural system, reducing dead loads, strengthening piers and foundations, etc.
Reinforcement plan determination principle
It is generally believed that the reinforcement scheme is basically feasible when the following conditions are met. Compared with the reconstruction of a new bridge, it can save a lot of investment and materials, and has obvious economic benefits; after the bridge is strengthened, it can meet the requirements in terms of structural performance, bearing capacity and durability; the substructure of the bridge has sufficient potential.
2 Several common methods of bridge reinforcement
2.1 Enlarged section reinforcement method
The enlarged section method, also known as the outer concrete reinforcement method, is a method of strengthening the section area and reinforcement of concrete structures. This reinforcement method requires the lower part of the bridge to be reinforced
The structure can bear more weight and provide higher bearing capacity. Under normal circumstances, it is mainly to thicken the bridge deck or enlarge the beam rib width of the main beam.
2.2 Prestressed reinforcement method
The pre-stressed reinforcement method is a method of strengthening the structure with externally pre-stressed steel tie rods. It is suitable for bridges that require improved bearing capacity, rigidity and crack resistance, and require less space after reinforcement. It can be divided into prestressed tie rod reinforcement and prestressed strut reinforcement. Among them, prestressed tie rod reinforcement is mainly used for bending members. The beam body is used as an anchor, and external force is applied to the tension area of the beam through prestressed tension to offset the self-weight of the structure and reduce the stress under the action of vehicle load. It can reduce excessive cracks in the beam and reduce the width of the cracks. The reinforcement of prestressed struts is mainly used for the axially compressed pier columns of the bridge substructure, but this method is rarely used in practice for the reinforcement of bridge pier columns.
2.3 External bonding steel reinforcement method
The external bonding steel reinforcement method is a reinforcement method that uses a chemical adhesive to directly paste the steel plate on the surface of the concrete member to form a force-bearing whole with the member to improve the bearing capacity, increase the ductility, rigidity and meet the requirements of normal use.
2.4 Pasting FRP reinforcement method
The bonding FRP reinforcement method is to use high-strength or high elastic modulus fiber composite materials, and use specially configured bonding resin or impregnating resin to paste on the surface of the bridge concrete member, so that it and the original member form an integral joint reinforcement method.
At present, there are three types of FRP materials commonly used in structural engineering: glass fiber (GFRP), carbon fiber (CFRP) and aramid fiber (AFRP), of which carbon fiber reinforced composite materials (CFRP) are used more. This article focuses on the use of CFRP reinforcement methods and practical engineering applications.
The fiber direction of carbon fiber cloth is divided into two kinds: unidirectional and bidirectional, among which unidirectional cloth is mainly used. Carbon fiber cloth has the characteristics of high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness-to-weight ratio, good fatigue resistance, high durability, corrosion resistance, and low thermal expansion coefficient.
When the reinforced bridge structure is in a special environment, other protective materials should be selected according to the specific conditions. At present, the reinforcement methods of pasting carbon fiber cloth are often supplemented by crack grouting and sealing methods.
Compared with other reinforcement methods, the advantages of carbon fiber cloth reinforcement technology are mainly reflected in: high strength and efficiency, strong designability; basically does not change the appearance of the original structure, and will not cause damage to the original structure; transportation, storage, and construction are more convenient and faster. It is easy to ensure the construction quality and low maintenance costs in the later period; its chemical structure is stable, and it is more prominent in weather resistance, corrosion resistance and fatigue resistance. However, when applying this method to strengthen the bridge, full consideration should be given to the orientation of the fibers, reasonable material connection method, connection size, connection location, and performance indicators of the bonding material. Especially the quality control of the construction process must be carried out in accordance with the normal construction procedures, otherwise it will affect the bridge reinforcement effect.
FRP reinforcement application examples
A bridge was built in the early 1970s: the superstructure is a 4-hole span L=16.8m, with a small reinforcement and micro-bent slab I-beam assembly type reinforced concrete beam structure. The bridge deck without crossbeam has a net clearance of 7m+ 2×0.25m. The lower structure is reinforced concrete double-column cast-in-place pile piers and gravity abutments.
Disease investigation before reinforcement
Before determining the reinforcement plan, a comprehensive investigation was carried out on the current situation of the old bridge, with 4×5 main beams of the whole bridge. According to the actual damage, the 15 main beams, micro-bent plates, supports, bridge piers (abutments) and auxiliary structures with 2 to 4 holes were carefully inspected.
Main beam
The construction quality is poor, and the size of each part is inconsistent along the span. A maximum of 51 cracks were found on a single main beam, and the width of the cracks was 4mm at most. There are vertical cracks, oblique cracks, and horizontal cracks. The angle between the oblique crack and the horizontal direction is 40-80. Vertical cracks are mainly distributed in the lower part of the main girder web (mainly within the range of 8.5m in the middle of the span), and are wide at the bottom and narrow at the top; oblique cracks are mainly distributed within 4m at the end; horizontal cracks are mainly distributed at the beam end. The local steel bars of the main beam are exposed, causing corrosion.
Reinforcement design
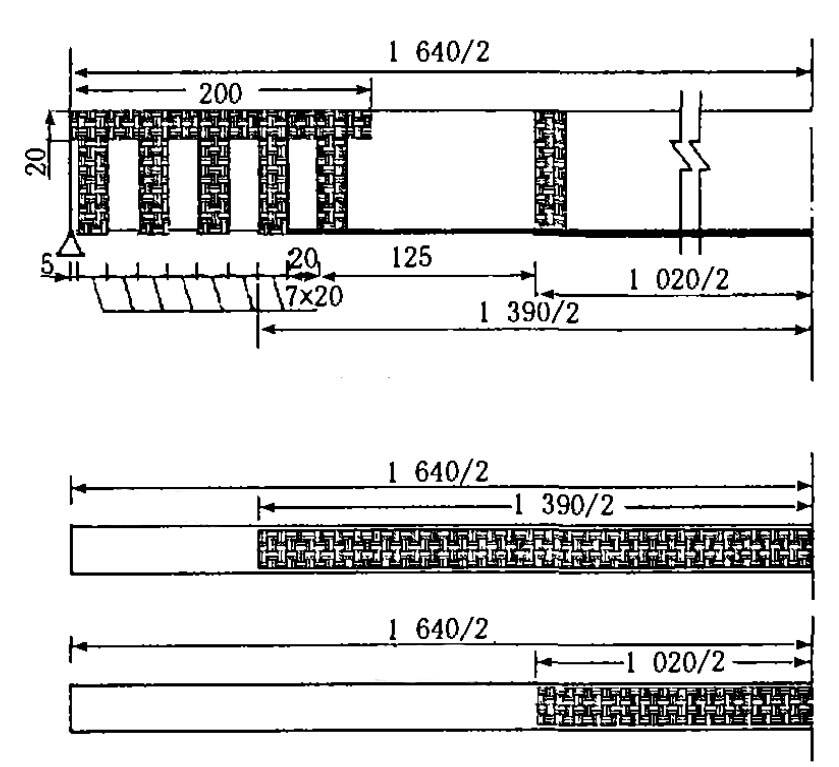
The main beam is reinforced with HM-30 carbon fiber sheet. The main performance indicators are: design thickness 0.167mm; tensile strength standard deviation 40MPa; tensile strength standard value 4108MPa; average tensile strength 4233MPa; elastic modulus 236GPa. In the calculation, taking into account the adhesion between the carbon fiber sheet and the main beam concrete, a reduction factor of 0.8 is used for the design value of the material's tensile strength. After calculation, the thickness of the bottom carbon fiber material in the middle of the main beam needs to be 0.25 mm, so two layers are used. The reinforcement design is shown in Figure 1.
Conclusion
This article introduces several main methods of strengthening old bridges, and focuses on the application of carbon fiber materials in strengthening old bridges. Through concrete reinforcement examples, it is shown that the bridge members reinforced with carbon fiber cloth can greatly improve the bending and shear resistance of the beams and plates, and can improve the stiffness and ductility of the bridge members, and play the role of restraining cracking and reducing deflection. I believe that this new material and new process will have greater application prospects after more engineering practice tests and improvements.
You can find anything here you are in need of, have a trust trying on these products, you will find the big difference after that.

High strength carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) strip / laminate / plate for structural strengthening and concrete repair

High strength, unidirectional carbon fiber sheet pre-saturated to form a carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) sheet used to strengthen structural concrete elements.

Two-components modified epoxy resin adhesive, with high quality plastic tube, double cartridge package for anchoring